Setup guide
This application consists of metabase, postgres, a webhook microservice, and a cron microservice. Going through this guide and setting this up on Hasura should take you about 15-10mins.
Pre-requisites:
- A Hasura account: register/login here.
- Follow the instructions to install and login with the hasura CLI.
- Enable billing on Hasura (the free tier on Hasura will not be able to run metabase).
Step 1: Fork & clone this repo
$ git clone git@github.com:hasura/issues.git
Step 2: Create a cluster
This command will create a Hasura cluster (2xCPU, 4GB RAM) in the San Francisco region.
Hit y when you’re asked for confirmation:
$ hasura cluster create -c hasura
This might take 10-15 mins and will create a cluster named something like juniper41.
This is what a successful output will look like:
• A new pro-tier Hasura cluster will be created [provider: digital-ocean, region: sfo2]
Nodes:
- s-2vcpu-4gb
Continue? (y/n) y
• Started provisioning cluster [juniper41]. This can take around 10-15 mins. Go ahead, grab a cup of coffee!
Completed 1/4: [juniper41] Creating a Kubernetes cluster
Completed 2/4: [juniper41] Initializing Hasura cluster
Completed 3/4: [juniper41] Syncing Hasura cluster
Completed 4/4: [juniper41] Generating SSL certificates
✓ Hasura cluster created name=juniper41
✓ SSH key (/Users/tanmaigopal/.ssh/id_rsa.pub) added to the cluster
✓ Git remote added to this repo name=hasura url=ssh://hasura@juniper41.hasura-app.io:22/~/git/juniper41
✓ You can now 'git push' to clusters [hasura]
✓ Cluster added to project cluster-alias=hasura cluster-name=juniper41
Step 3a: Setup the github token secret
Create a github token
Grab your github token from https://github.com/settings/tokens.
Create a token that has read access to your orgs/repos.
Let’s say the token is 123whatamagicalsecret789.
Set up a secret
Setup the secret on your cluster:
$ hasura secrets update github.token 123whatamagicalsecret789
Step 3b: Setup the github org environment variable
The github org environment variable is in a kubernetes manifest file.
Head to microservices/app/k8s.yaml and around Line#30 edit the environment variable called GITHUB_ORG:
- name: GITHUB_ORG
value: "my-github-org"
Step 4: Deploy
You’re all setup. Let’s deploy all the microservices and the postgres tables/views to the cluster:
$ git push hasura master
This might take a few minutes for all the python docker images to build.
Once this is done, to check if everything worked successfully, you can check if the right tables and views got created.
$ hasura api-console
• Trying to open console in browser. If it doesn't work, open the below URL manually:
• Console URL: http://localhost:9695
This will open up a browser that is running an admin UI. Head to localhost:9695/data and check if a bunch of tables have gotten created.
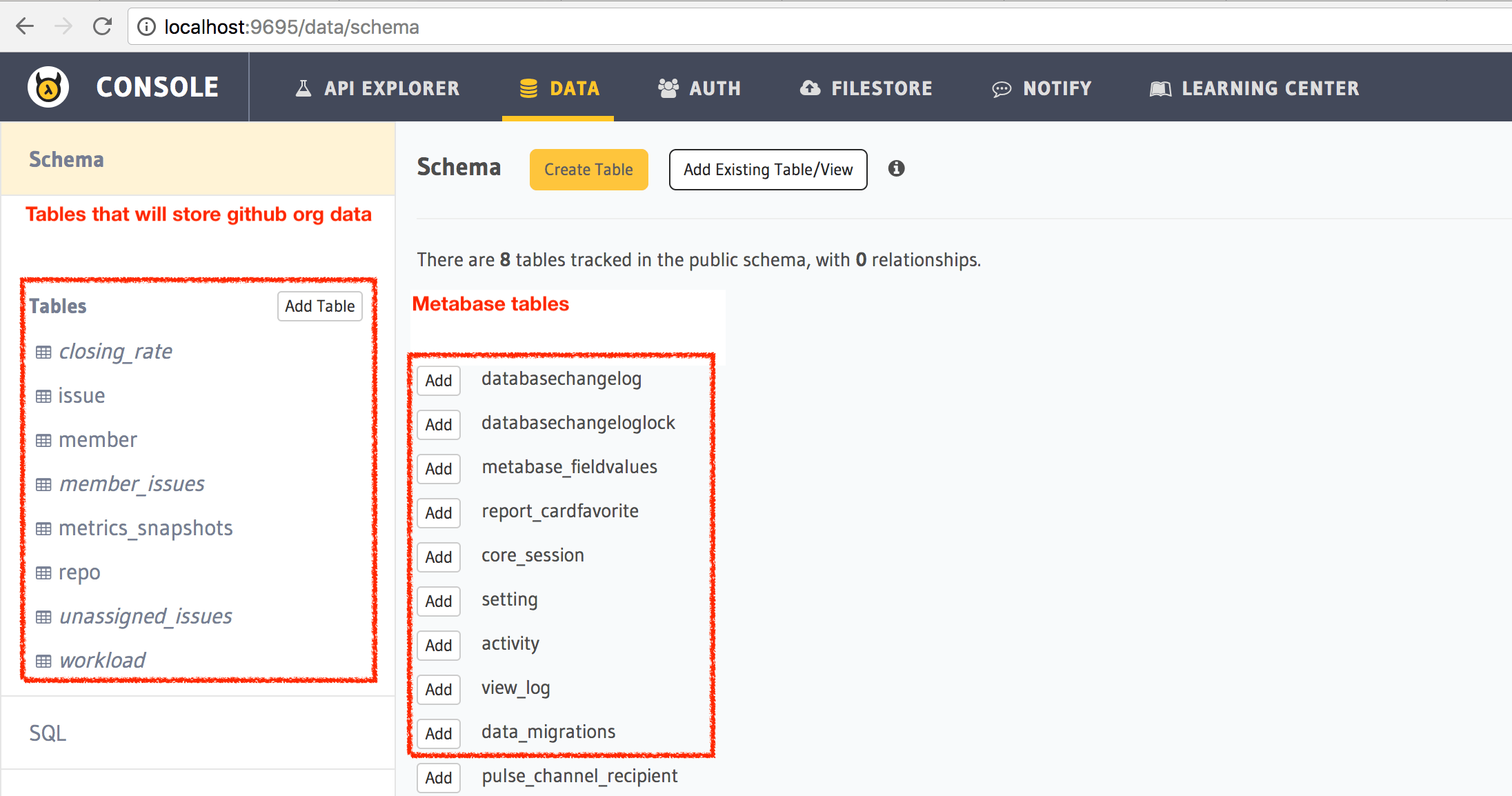
Step 5: Initialise data from your github org
The app microservice running on the cluster has a bunch of APIs that help with data initialisation.
# Open the app microservice URL:
$ hasura microservice open app
✓ https://app.juniper41.hasura-app.io/ opened in browser
This will open up the browser at a URL like: app.clusterName.hasura-app.io.
Click on the API calls mentioned on the page to start initialising your data.
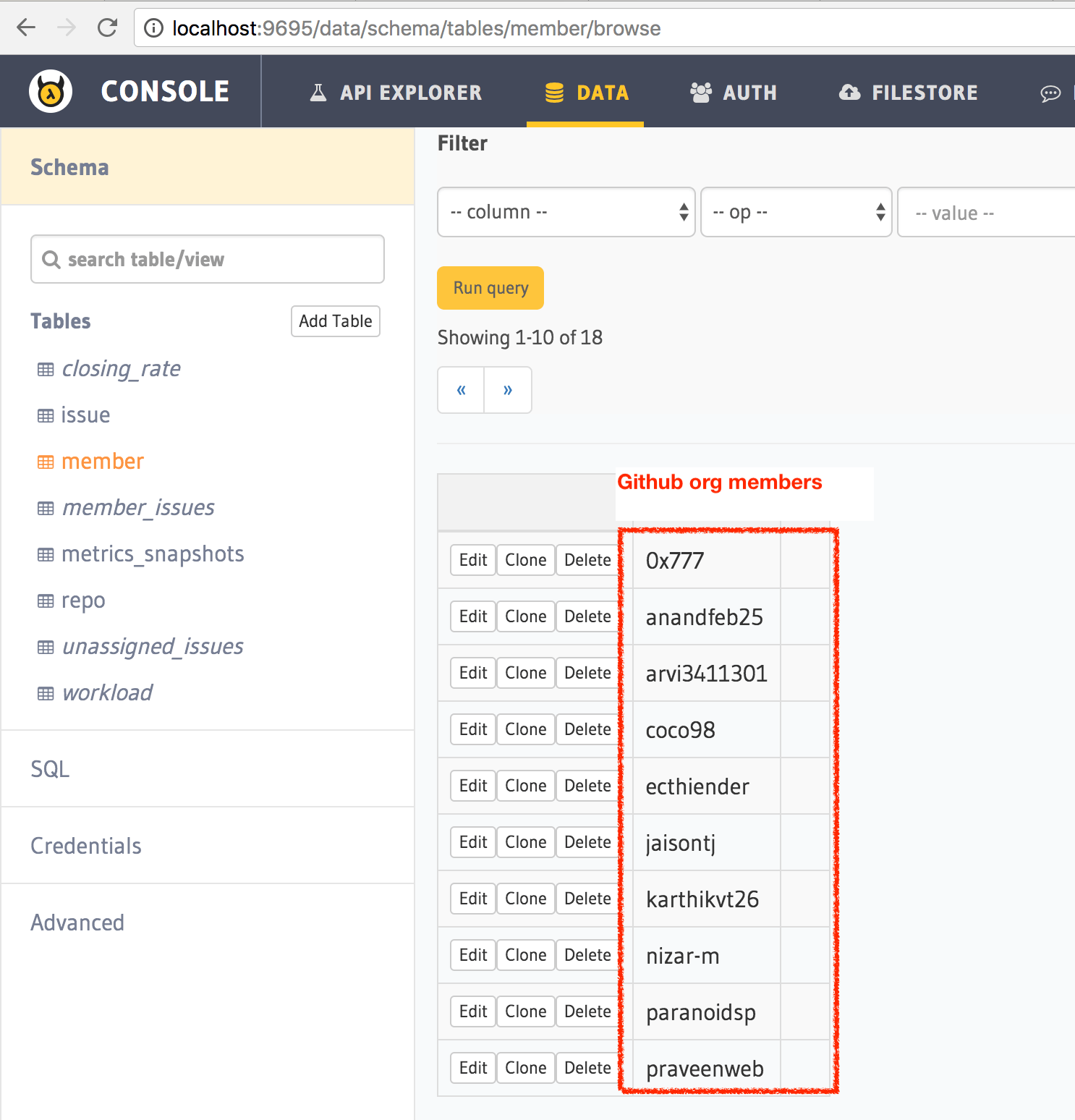
Once you do this and head back to the api-console you’ll see that the tables now have data.
For example: http://localhost:9695/data/schema/tables/member/browse
Step 6: Initialise metabase
Open up the metabase microservice:
$ hasura microservice open metabase
✓ https://metabase.juniper41.hasura-app.io/ opened in browser
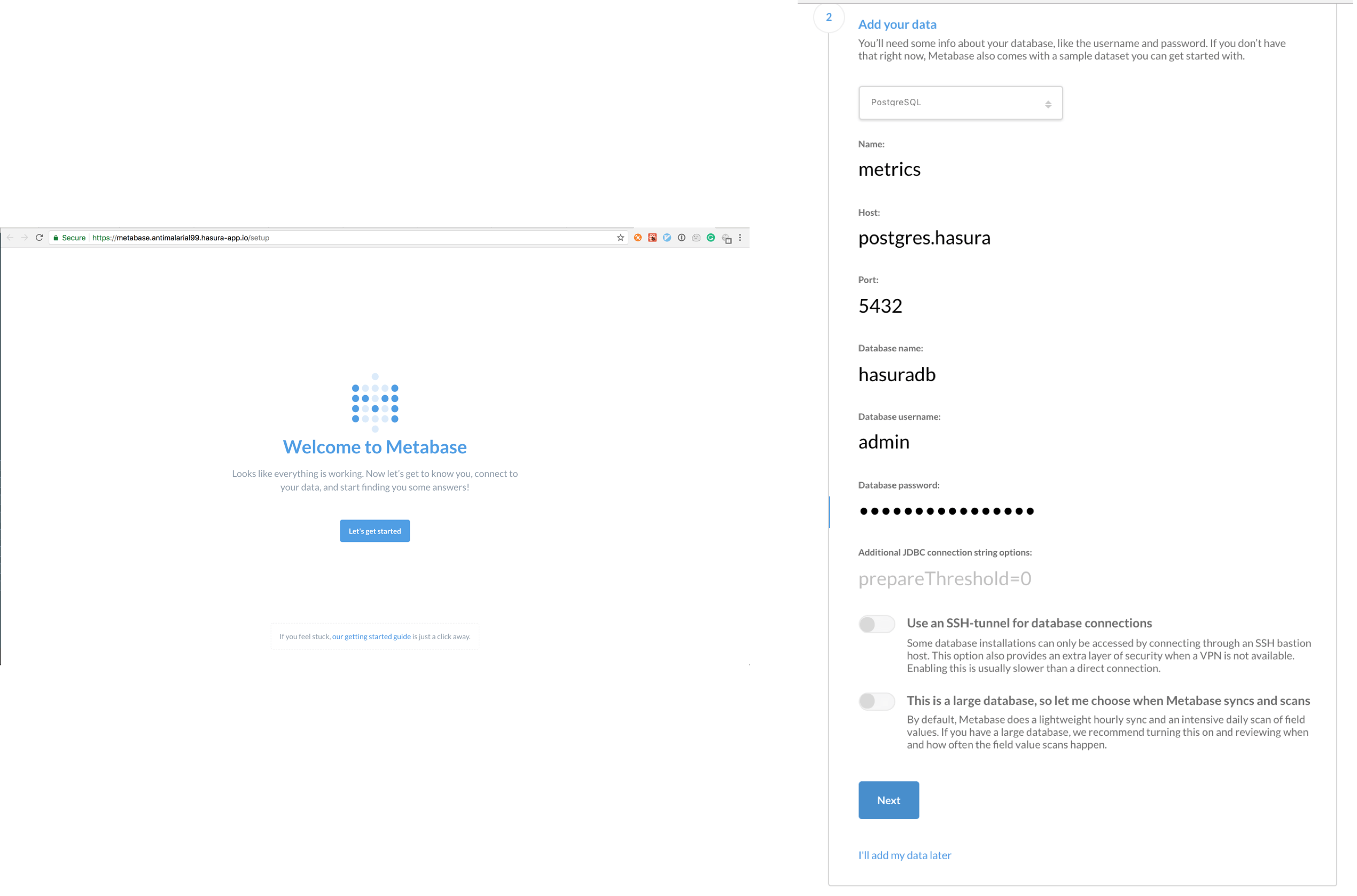
Metabase takes a while to startup, so if you see a 502/504 for a minute or two, don’t panic. Once you see the metabase setup screen, these are the important values you need to have to link it to postgres:
- host:
postgres.hasura - port:
5432 - username:
admin - password: Get the password by running
hasura secrets lsand you’ll see an entry calledpostgres.password. - database:
hasuradb
Step 7: Create metabase questions
That’s it. Once you’re logged in, start creating questions and browsing data metabase style.
Step 8: Install the webhook on your github account so that you can keep up to date with issues
Head to your webhooks section on github:
https://github.com/organizations/my-org/settings/hooks
Add webhook:
Set this URL as a webhook that can listen to changes on repos and issues.
https://app.clusterName.hasura-app.io/webhook
Note: Replace my-org and clusterName with the right values.
Test it out:
Create an issue and head to the issues table and see that it got added. The issues table in your API console would be at: http://localhost:9695/data/schema/tables/issue/browse